For decades, gout sufferers have been told a simple rule: avoid beer at all costs. This blanket prohibition has left millions of people wondering if they can ever enjoy a cold brew again. After conducting extensive research into the latest scientific studies, brewing technologies, and clinical data, we can finally provide definitive answers about what really causes gout flares in beer and which options are genuinely safe for gout sufferers.

A medical illustration shows the inflamed big toe joint in a foot affected by gout, detailing uric acid crystals and tophi deposits mana
Table of Contents
Executive Summary: The Position on Safe Beer Consumption for Gout Sufferers
The bottom line: Most traditional beers pose significant gout risks, but breakthrough Japanese zero-purine beers offer a genuinely safe alternative that allows gout sufferers to enjoy beer without triggering flares.
Traditional beer contains 225-580 mg/L of purines—primarily guanosine—which directly convert to uric acid in the body 12. However, Japanese brewers have developed enzymatic technologies that eliminate virtually all purines, creating beers with 0-4 mg/L purine content 34. These zero-purine beers, including Kirin Zero, Sapporo Zero, and Asahi W-Zero, represent the first truly gout-safe beer options in history 56.
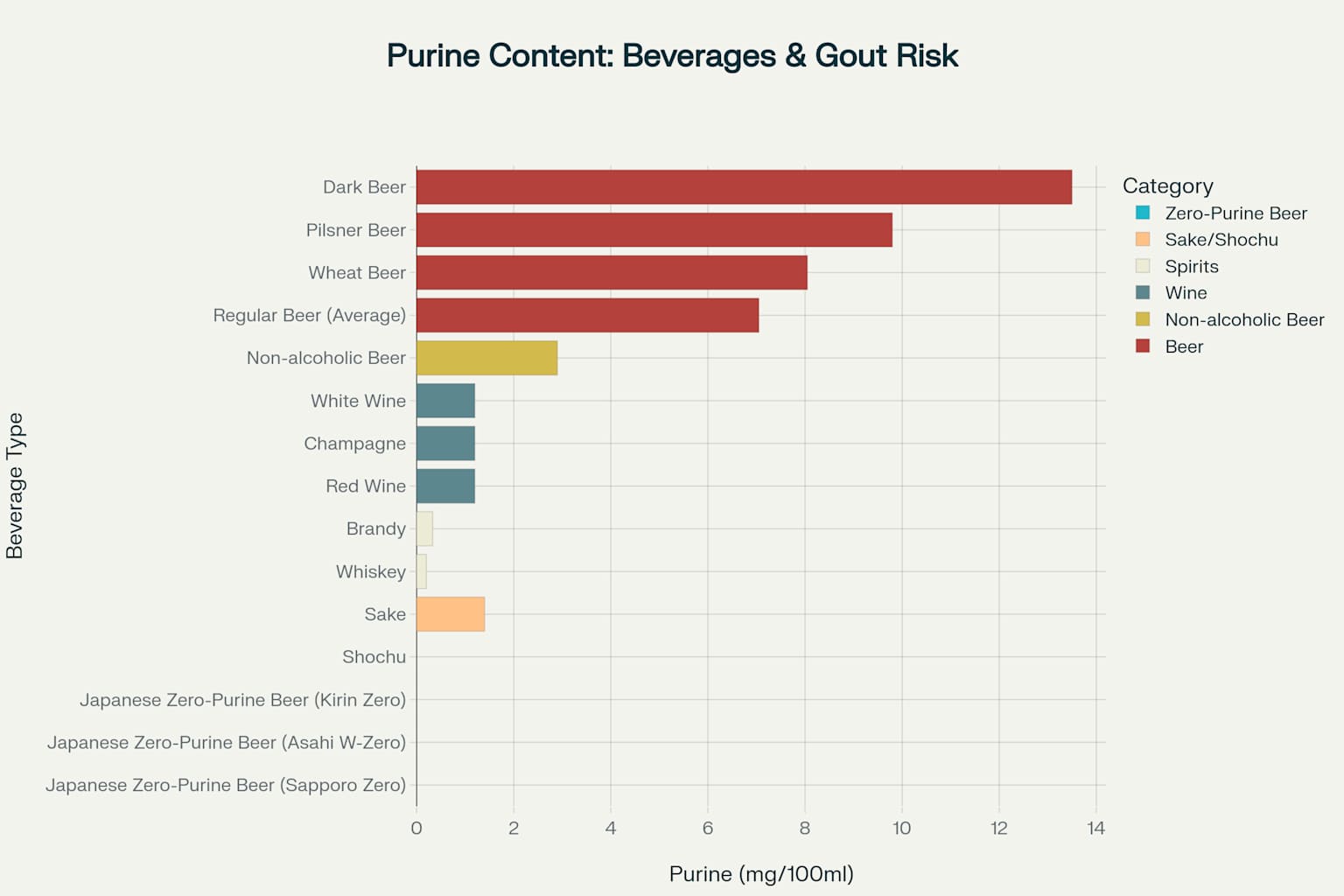
Purine content comparison across alcoholic beverages showing Japanese zero-purine beers as the safest option for gout sufferers
Myth-Busting: What Really Causes Gout in Beer
Myth 1: "It's the alcohol, not the beer itself"
Fact: While alcohol does contribute to gout through metabolic effects, the primary culprit in beer is its extraordinarily high purine content 17. Beer contains 10-50 times more purines than wine or spirits 89. A single beer can contain 7-13.5 mg/100ml of purines, compared to just 0.2-1.4 mg/100ml in wine and spirits 810.
Myth 2: "All alcoholic beverages are equally bad for gout"
Fact: Beer is uniquely problematic due to its purine profile 1112. Large-scale studies show beer increases gout risk at any dose, while moderate wine consumption may actually be protective 1213. Beer drinkers have a 55% higher gout risk per pint daily compared to wine drinkers, who showed reduced risk with moderate consumption 11.
Myth 3: "Non-alcoholic beer is safer for gout"
Fact: Many non-alcoholic beers contain higher purine levels than regular beer 1415. The dealcoholization process often concentrates purines, making these "healthier" options potentially worse for gout sufferers 14. Only Japanese zero-purine varieties are specifically engineered to eliminate purines entirely 516.
Myth 4: "The sugar in beer causes gout"
Fact: Beer's sugar content has minimal impact compared to its purine load 17. While fructose can contribute to uric acid production, beer contains relatively small amounts of sugars 1718. The primary driver remains the direct purine-to-uric acid conversion pathway 12.
The Science: Multiple Pathways to Gout

Modern stainless steel fermentation tanks inside a clean brewing facility yolongbrewtech
Beer triggers gout through multiple interconnected mechanisms, but they are not all equally important.
Primary Mechanism: Direct Purine Content (High Impact)
Beer's purine content is the dominant factor 12. During brewing, nucleic acids from malt and yeast break down into purine compounds, primarily guanosine 119. These purines are then metabolized directly into uric acid by the enzyme xanthine oxidase 120. Regular beer contains 400+ mg/L of purines, creating a massive uric acid burden 218.
Secondary Mechanisms: Alcohol Metabolism (Medium Impact)
Minor Mechanism: Fructose Effects (Low Impact)
Small amounts of sugars in beer can activate the fructose pathway, leading to ATP depletion and increased uric acid synthesis 1726. However, this contribution is minimal compared to direct purine content 17.

Laboratory equipment for precise analysis of beverage composition com
Beer Types and Gout Risk Assessment
Not all beers pose equal risks. Scientific analysis reveals a clear hierarchy:
Highest Risk (Score: 10/10)
High Risk (Score: 9/10)
Medium-High Risk (Score: 7/10)
Medium Risk (Score: 6/10)
Light beers (<4% ABV): Reduced alcohol but standard purine levels
Low Risk (Score: 3/10)
Minimal Risk (Score: 1/10)
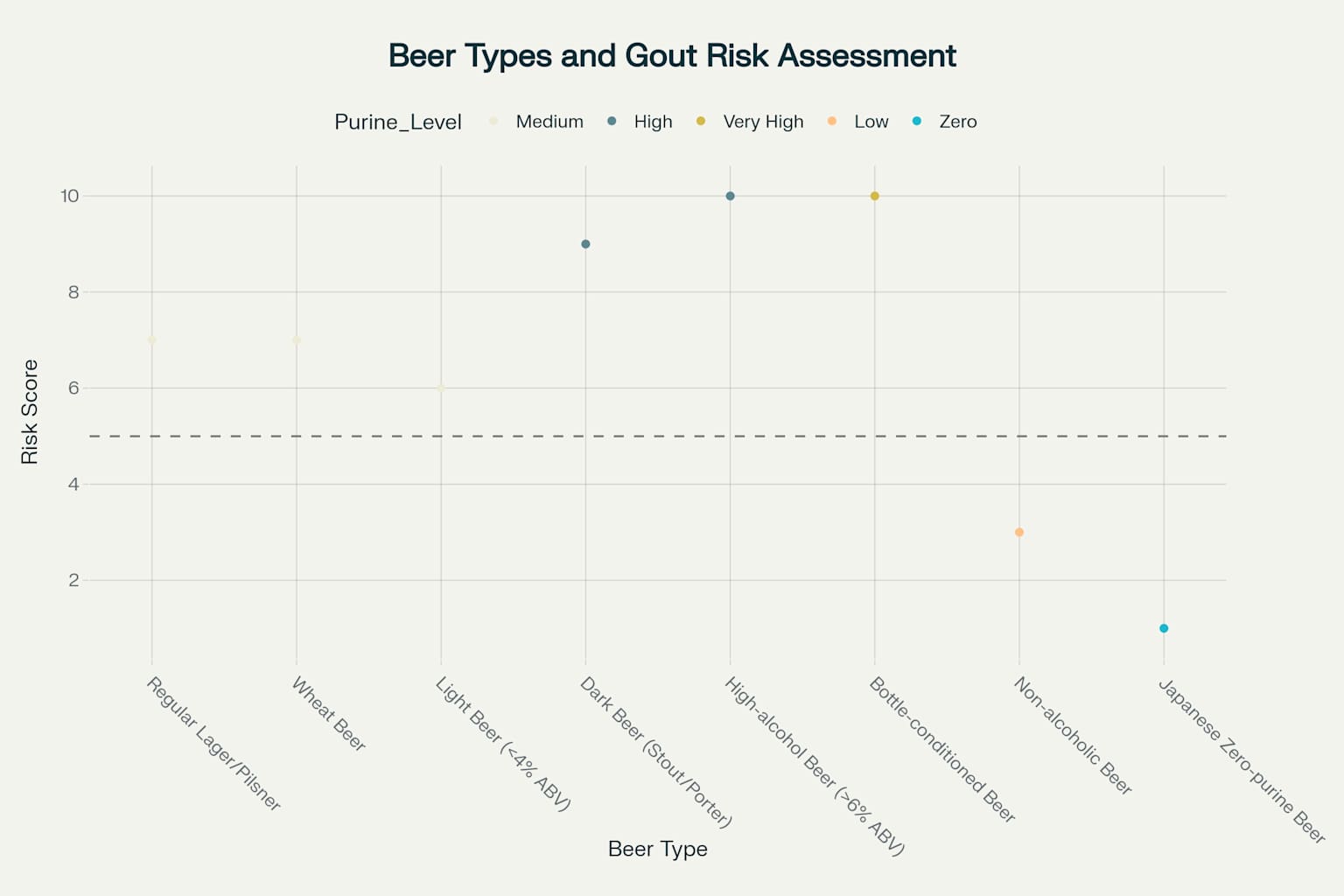
Risk assessment of different beer types for gout sufferers, highlighting Japanese zero-purine beers as the safest option
Continue reading about Japanese zero-purine beer technology after the break.
The Japanese Innovation: Zero-Purine Beer Technology

Bottles of popular Japanese beers Sapporo, Asahi, and Kirin Ichiban shown for reference in a discussion about beer ingredients and gout dreamstime
Japanese brewers have revolutionized beer production for gout sufferers through breakthrough enzymatic technologies 34. The key innovation involves purine nucleoside phosphorylase (PNP) derived from the mushroom Agaricus bisporus 34.
How Zero-Purine Beer Is Made
The process involves treating wort with AbPNP enzyme during saccharification, which reduces purine nucleosides by 33.54% while increasing yeast utilization of remaining purine bases 34. This dual action virtually eliminates purines while maintaining beer flavor and actually improving alcohol content by 3.6% 34.
Available Zero-Purine Options
Japanese brewers now offer multiple truly gout-safe options 5:
Sapporo Zero: 100% purine-free, alcohol-free option 5
These products are available online and at specialty stores, representing the first genuinely safe beer options for gout management 5.

Collection of five Japanese beer cans including Sapporo, The Premium Malt's, Yebisu, Asahi Super Dry, and Kirin Beer 88bamboo
Clinical Evidence: Real-World Impact
Epidemiological Studies
Large-scale research consistently demonstrates beer's unique gout risk 1129. The UK Biobank study of 401,128 participants found beer consumption associated with higher gout risk in both sexes, with beer showing the strongest association per serving compared to other alcoholic beverages 1129.
Metabolic Studies
Clinical trials reveal beer's dual impact on uric acid metabolism 130. A controlled study showed beer consumption increased plasma uric acid by 13.6% and enhanced 24-hour uric acid excretion, confirming both increased production and altered kidney function 1530.
Practical Recommendations for Gout Sufferers
Safest Choices (Recommended)
Moderate Risk (Proceed with Caution)
Avoid Completely
High-alcohol beverages that amplify all gout mechanisms
Bottle-conditioned or unfiltered beers with living yeast 27
Timing Considerations
For those on uric acid-lowering medications like allopurinol, occasional consumption may be possible after six months of stable treatment 32. However, zero-purine alternatives eliminate this risk entirely 54.
The Future of Gout-Safe Brewing

Modern stainless steel tanks and cooling units used in a brewery for beer production yolongbrewtech
Research continues into purine reduction technologies 3334. University teams are developing genetically engineered yeasts with enhanced purine absorption capabilities 34. Additional enzymatic approaches using adenine deaminase and guanine deaminase show promise for further reducing beer purine content 3536.
Patent applications reveal ongoing innovation in low-purine brewing methods, including acid hydrolysis techniques that increase free purine ratios for improved yeast utilization 37.
Conclusion: A New Era for Gout Sufferers
The longstanding prohibition against beer for gout sufferers is no longer absolute. While traditional beers remain problematic due to their high purine content (the primary mechanism), Japanese zero-purine beers offer a genuine solution. These products eliminate the main cause of beer-induced gout while preserving taste and drinking experience.
The key breakthrough understanding is that beer's gout risk stems primarily from its purine content, not alcohol or sugar content. This knowledge has enabled targeted solutions that address the root cause rather than requiring complete avoidance.
For the first time in history, gout sufferers have access to genuinely safe beer options that don't compromise their health management goals. The choice between continued prohibition and innovative alternatives is now in the hands of informed consumers and their healthcare providers.
The future of beer consumption for gout sufferers is not about elimination—it's about education and better choices.
